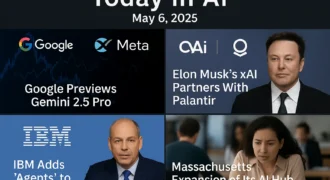
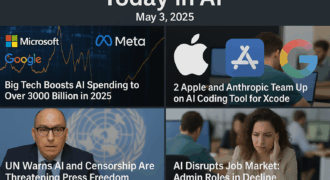
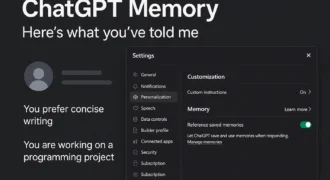
Cambridge, MA — Researchers at MIT have developed a new framework that dramatically improves how accurate and reliable code generation by large language models (LLMs) can be. The technique makes it possible for even smaller AI models to produce syntactically correct and functionally sound code — potentially changing the way developers use AI-assisted coding tools across various domains.

(Reference image)
AI-generated code has made serious progress in recent years, but one problem persists: language models tend to produce flawed outputs — sometimes full of syntax errors, sometimes just logically wrong. Existing approaches to force better outputs from these models are often inefficient or too restrictive, reducing the creativity and flexibility of the AI. That’s where the new MIT framework comes in.
Instead of relying on brute-force generation or heavy constraints, the team introduced a probabilistic method that allocates computational effort more strategically. Promising code paths are explored deeper, while weaker ones are discarded early in the generation process. The result? Better code with fewer bugs — and less computational waste.
Smarter, Smaller, More Efficient
One of the biggest advantages of the approach is how well it performs even when applied to smaller language models. In multiple test scenarios — ranging from molecular biology tools to robotics applications — the MIT method allowed leaner models to outperform much larger ones in both accuracy and speed. This not only improves developer productivity but also opens the door to more accessible AI systems for companies and individuals without massive computing budgets.
What makes this especially powerful is its potential for non-experts. Imagine business analysts using natural language prompts to generate SQL queries that work — without ever needing to learn SQL. The framework brings that possibility closer to reality, turning AI from an assistant for coders into a tool for anyone working with structured data or logic-based systems.
The researchers plan to integrate the method into existing AI tools soon. If successful, it could sharply reduce debugging time and allow companies to build faster, more reliable systems powered by lightweight AI models.
What It Means for the Future of AI-Assisted Development
This innovation doesn’t just fix a technical issue — it reflects a broader trend in the AI world: smarter, more context-aware tools that are designed not just for engineers, but for everyone. By reducing complexity and increasing reliability, MIT’s contribution could shape the next generation of coding platforms, where AI becomes an everyday collaborator — not just a clever gimmick.

Christoph
Explores the future of AI
Sharing insights, tools, and resources to help others understand and embrace intelligent technology in everyday life.