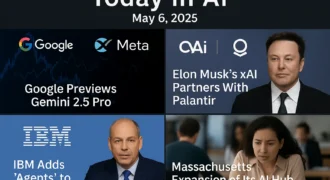
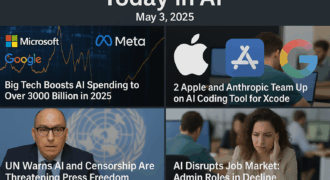
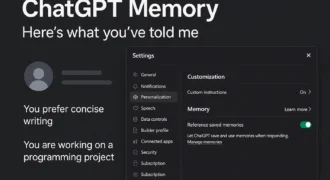
Huawei’s Ascend 910B Chip Threatens Nvidia’s AI Leadership
Huawei has unveiled an advanced AI chip that rivals Nvidia’s H100, challenging U.S. dominance in high-performance AI hardware. Huawei has launched the Ascend 910B, a next-generation AI chip that appears to match the computational performance of Nvidia’s widely used H100. This development signals a major stride in China’s quest to reduce its reliance on American semiconductor technology, especially amid tightening U.S. export restrictions.
The Technical Edge
While Huawei has not released official benchmarks for the 910B, industry insiders suggest it is built on a 7nm process, possibly using technology from China’s Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC). The chip reportedly supports high memory bandwidth and features an architecture optimized for deep learning tasks.
Global Implications
The emergence of the 910B could shift the competitive landscape in the AI hardware sector. While Nvidia still dominates the global market, especially in Western countries, Huawei’s chip offers a viable domestic option for Chinese enterprises and research institutions cut off from U.S. technologies. Moreover, China’s push for semiconductor independence may soon result in a more fragmented global AI infrastructure, with Western and Chinese ecosystems developing in parallel. The geopolitical consequences of this divergence are still unfolding, but Huawei’s latest move is a clear signal of intent. While Huawei faces ongoing U.S. sanctions and continues to be blacklisted from purchasing advanced lithography equipment, its chip development shows that domestic innovation in China’s tech sector is gaining ground — particularly in AI, where computational demand is rapidly increasing worldwide.
Christoph
Explores the future of AI
Sharing insights, tools, and resources to help others understand and embrace intelligent technology in everyday life.