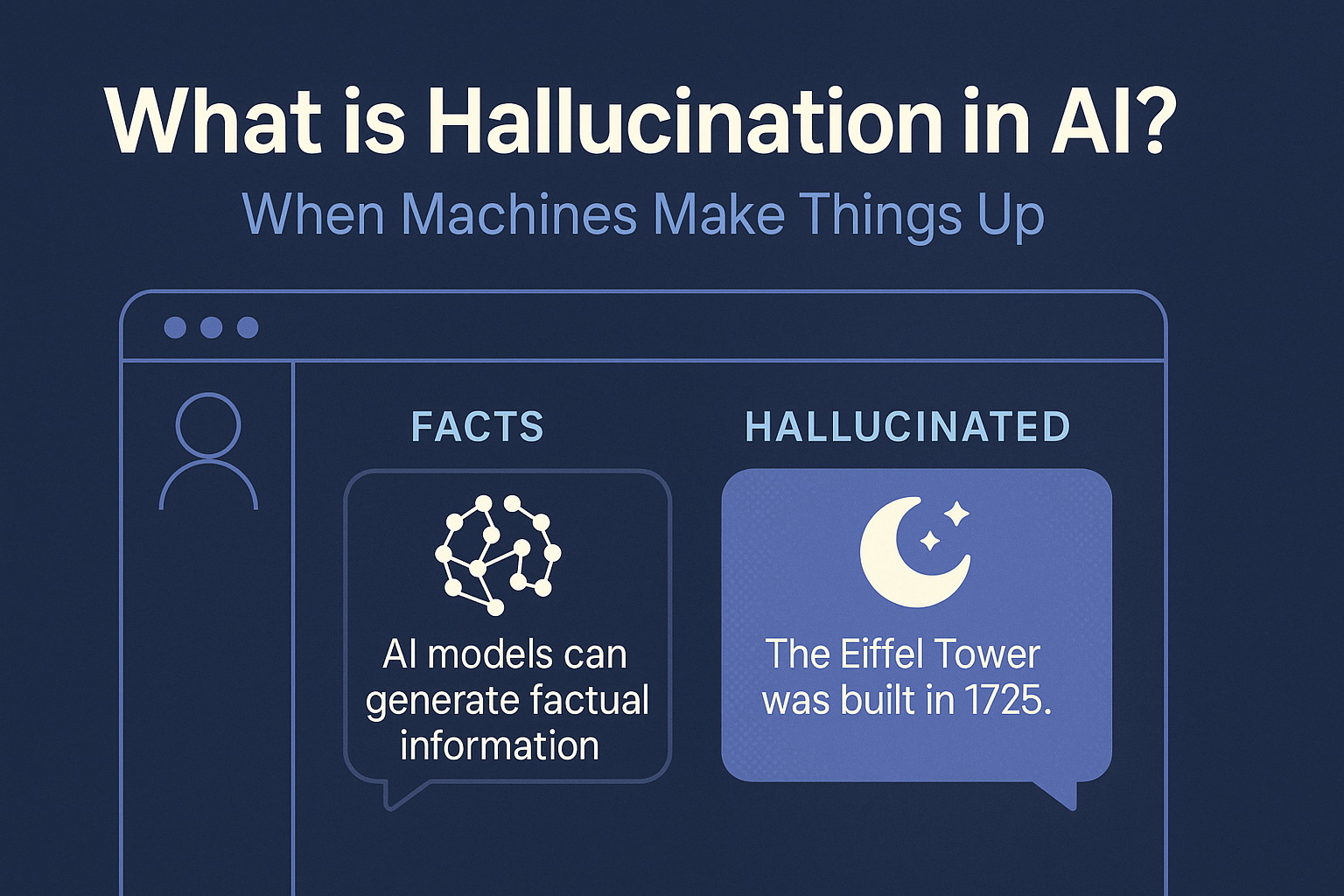
What is Hallucination in AI?
One of the more surprising behaviors of modern AI systems is their tendency to sometimes produce information that sounds entirely plausible—but simply isn’t true. This phenomenon is known as hallucination in AI. It refers to moments when a model, instead of accurately recalling facts or logic, fabricates details, invents references, or confidently states incorrect information.
Hallucinations are especially common in large language models like ChatGPT, which are trained to predict patterns of words rather than verify facts. These systems aim to continue conversations smoothly, even if that sometimes means filling in gaps with fictional or inaccurate content rather than admitting a lack of knowledge.
Several factors contribute to hallucination. Often, the training data may be incomplete, prompting the AI to guess based on related patterns rather than known facts. Vague or ambiguous prompts can also lead to confident but fabricated answers. And because current models are not built with integrated fact-checking mechanisms, they can deliver responses that sound credible without actually being grounded in reality.
Hallucinations can have serious consequences. In fields like healthcare, education, and law, relying on incorrect information could cause real harm. That’s why reducing hallucination rates is a major focus in AI development today. Techniques to address the issue include training models on higher-quality datasets, allowing AI systems to cite their sources, and combining generative models with real-time search tools or external databases.
🔎 In a Nutshell
AI hallucination happens when a system generates convincing but false information. It’s one of the biggest challenges facing trustworthy AI today—and solving it is crucial to ensuring these technologies are safe, reliable, and beneficial.
📚 For more foundational terms and concepts, check out our full AI Glossary.